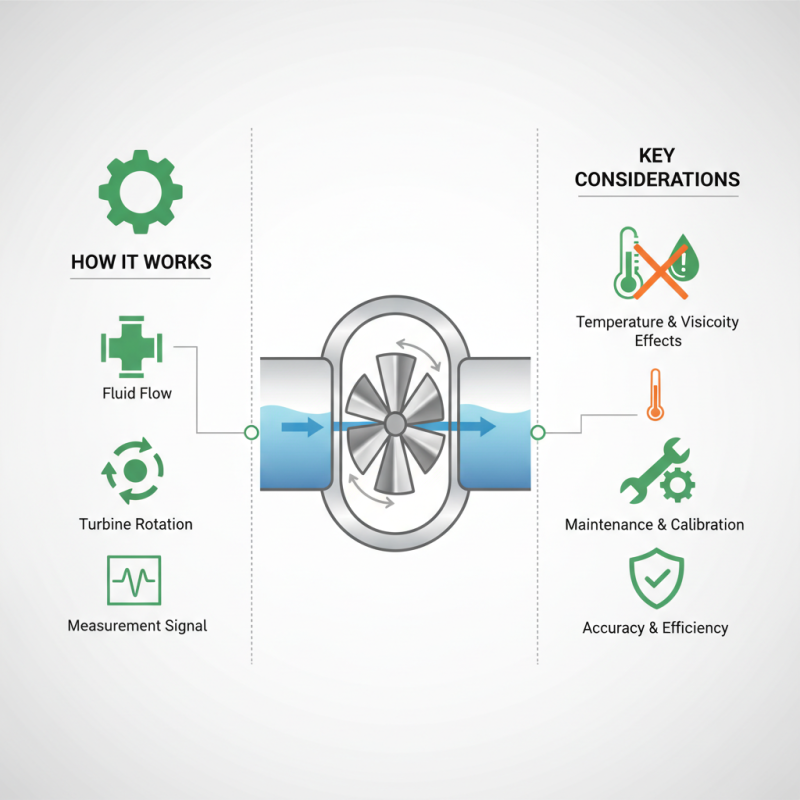
What is a Turbine Flow Meter and How Does it Work?
A Turbine Flow Meter is an essential device in fluid measurement. It plays a vital role in various industries. These include water treatment, oil, and gas. Understanding how it works can enhance efficiency in operations.
At its core, a Turbine Flow Meter uses a rotating turbine to measure flow rates. The fluid flows through the meter, causing the turbine to spin. This rotation is proportional to the flow rate. Simple, yet effective. However, factors like viscosity and temperature can affect accuracy.
Users often overlook these aspects. Inaccurate readings can lead to costly errors. It's crucial to maintain and calibrate the meter regularly. Recognizing potential pitfalls is vital for optimal performance. Overall, a Turbine Flow Meter is an invaluable tool, but it requires careful handling.
What is a Turbine Flow Meter?
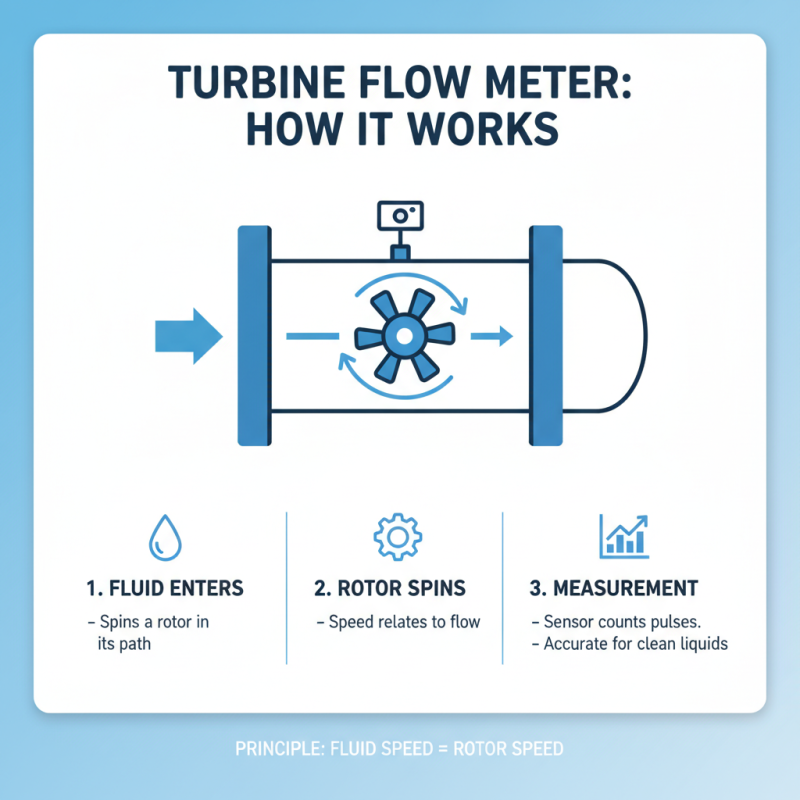
A turbine flow meter is an instrument used to measure fluid flow rates. It operates based on a simple yet effective design. When fluid passes through the meter, it spins a rotor placed in the flow path. The speed of the rotor correlates directly with the flow rate. This mechanism makes turbine flow meters highly accurate, especially for clean fluids.
According to industry reports, turbine flow meters provide accuracy levels within 0.5% of the reading, making them reliable for various applications. They excel in applications involving water, oils, and chemicals. However, they are not ideal for measuring viscous or dirty fluids, as debris can affect performance. Users must ensure the flow is free of contaminants for optimal accuracy.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential. Check for wear on the rotor and clean the meter regularly. Periodic calibration also improves accuracy. If you notice unusual readings, investigate potential issues. This step can save time and resources. Remember that even the best flow meters have limitations. Understanding these helps in making informed decisions.
Components of a Turbine Flow Meter
A turbine flow meter consists of several key components.
The heart of the meter is the turbine rotor. It spins as fluid flows through it.
The speed of rotation is directly proportional to the flow rate.
Next, the housing encapsulates the rotor, directing the fluid's path.
This ensures accurate measurement.
Sensors are essential. They detect rotor speed and convert it into an electronic signal.
This signal gets processed and can be displayed. Additionally, there are bearings and seals.
They support the rotor, allowing for smooth motion.
High-quality components enhance the meter's durability and accuracy.
Tips: Regular maintenance is crucial.
Check for wear and tear on seals and bearings.
A worn component can lead to inaccuracies.
Also, calibrate the meter periodically. This ensures it provides reliable readings.
Remember, a clean installation environment matters.
Dust and debris can interfere with accuracy.
How Turbine Flow Meters Measure Fluid Flow
Turbine flow meters are widely used devices for measuring fluid flow in various applications. They operate on a simple, yet effective principle. As fluid passes through the meter, it drives a turbine. This turbine then rotates at a speed proportional to the flow rate. It's a clear and direct relationship; higher flow means faster rotation.
The measurement process is straightforward, but it has nuances. Each revolution of the turbine is counted. This count is converted into a flow rate. Factors like fluid viscosity and density can affect accuracy. Not every fluid behaves the same way. For example, thick liquids might not spin the turbine as efficiently as water does.
Installation is crucial for proper function. If the flow meter is not aligned, it can give false readings. Frequent maintenance checks are necessary as well. Dust and debris can build up, impacting performance. Understanding these elements can lead to better usage and selection of turbine flow meters. There is always room for improvement in accuracy and reliability.
Applications of Turbine Flow Meters

Turbine flow meters are crucial in various industries, such as oil and gas, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals. They measure the flow rate of liquids and gases with high accuracy. According to industry data, turbine flow meters can achieve an accuracy within ±0.5% to ±1%. This precision makes them ideal for applications requiring exact measurements.
In the oil and gas sector, turbine flow meters are commonly used for custody transfer. They ensure that the amount transferred meets agreed measurements. Additionally, in water management, these meters help monitor and regulate water supply. The accuracy in this application helps prevent wastage and ensures sustainability.
**Tip:** Regular calibration is essential for maintaining accuracy. A small error can lead to significant financial losses over time.
In pharmaceuticals, these meters play a role in processes like mixing and quality control. Precise flow measurements are critical in maintaining product consistency and compliance with health regulations. However, it's important to account for factors that might affect performance, like viscosity changes in liquids.
**Tip:** Always consider the fluid properties when selecting a turbine flow meter. This factor can greatly influence measurement outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Turbine Flow Meters
Turbine flow meters are popular devices used to measure fluid flow. They offer several advantages that make them attractive for various applications. One key benefit is their high accuracy. These meters can provide precise flow readings, crucial for industries like oil and gas. Additionally, they respond quickly to changes in flow conditions, ensuring real-time monitoring.
However, turbine flow meters have limitations. They can struggle with low flow rates, leading to inaccuracies. This becomes a critical issue in small pipelines or when dealing with viscous fluids. Maintenance is another consideration. Turbine meters contain moving parts, which may wear out over time. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent failures.
Moreover, they might not perform well in pulsating flows. This limits their use in certain situations. Overall, while turbine flow meters have distinct advantages, users must weigh these against potential drawbacks. The choice should depend on specific application needs and conditions.
What is a Turbine Flow Meter and How Does it Work? - Advantages and Limitations of Turbine Flow Meters
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Type of Meter | Turbine Flow Meter |
| Operating Principle | Measures flow rate by the rotational velocity of a turbine. |
| Measurement Range | Typically 0.1 to 15 m/s |
| Flow Types | Liquid and Gas |
| Accuracy | ±1% to ±2% of reading |
| Advantages | High accuracy, good repeatability, suitable for a wide range of fluids. |
| Limitations | Susceptible to pressure changes, may require straight-run piping for accuracy. |
| Applications | Water supply, oil and gas, food and beverage industries. |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration required, cleaning may be necessary for viscous fluids. |
Related Posts
-

What is the Working Principle of a Turbine Flow Meter
-

Understanding Common Challenges with Magnetic Flow Meters for Global Buyers
-

Innovative Alternatives to Inline Flow Meter Solutions for Enhanced Measurement Accuracy
-

How to Select the Best Turbine Meter for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Mag Meter for Your Industrial Needs
-

Innovative Solutions for Magnetic Flow Meter Applications Showcased at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
