Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Electromagnetic Flow Meter for Your Needs
In the realm of industrial measurement, selecting the appropriate Electromagnetic Flow Meter is crucial for optimizing processes and ensuring accuracy. According to Dr. John Smith, a leading expert in flow measurement technology, "The right Electromagnetic Flow Meter can significantly enhance operational efficiency by providing accurate flow data, which is essential for effective decision-making." As industries evolve and demands increase, understanding the fundamental characteristics and features of Electromagnetic Flow Meters becomes increasingly important.
When it comes to choosing the right Electromagnetic Flow Meter for your specific needs, the decision-making process can be daunting. Factors such as the fluid type, operating conditions, and required accuracy levels all play a pivotal role in determining the most suitable meter. However, with the right guidance, selecting an Electromagnetic Flow Meter can be streamlined, allowing you to focus on efficiency and productivity in your operations. In this article, we will explore the top ten tips that will aid you in making an informed choice in the vast market of flow measurement technologies.

Understanding the Basics of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
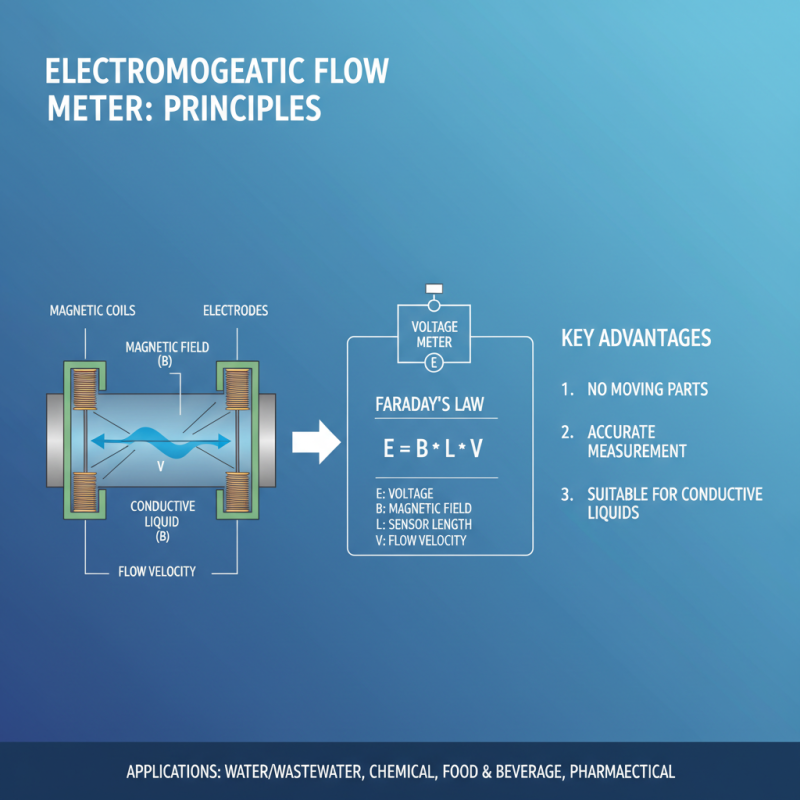
Electromagnetic flow meters are widely used in various industries for measuring the flow rate of conductive liquids. Understanding the basic principles behind these meters is essential for selecting the right one for your specific needs. These devices operate on Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction, where a conductive fluid moving through a magnetic field generates a voltage proportional to its flow velocity. This principle allows for accurate flow measurements without any moving parts, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
When considering a flow meter, it’s crucial to assess the characteristics of the fluid being measured, including its conductivity, temperature, and pressure. Electromagnetic flow meters are particularly effective for fluids with higher conductivity, such as water and slurry, but may not be ideal for non-conductive liquids. Additionally, installation requirements, including pipe size and orientation, must be taken into account, as these factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of the measurements. By grasping these foundational concepts, users can make informed decisions and choose an electromagnetic flow meter that best fits their operational needs.
Key Applications and Industries for Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Electromagnetic flow meters have become essential instruments in various industries due to their accuracy and reliability in measuring the flow of conductive fluids. Key applications include water and wastewater management, where they play a critical role in monitoring and controlling the flow of treated and untreated water.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the water and wastewater segment is projected to dominate the electromagnetic flow meter market, accounting for over 40% of the total demand by 2025. This growth is driven by increasing concerns for clean water supply and the need for efficient monitoring solutions in municipal services.
Another significant application area is the pharmaceuticals and food and beverage sectors, where process integrity is crucial. Electromagnetic flow meters offer non-intrusive flow measurement, ensuring the continuous monitoring of viscous fluids without contamination risks. Research from Grand View Research indicates that the pharmaceutical industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2020 to 2027, further increasing the demand for reliable flow measurement solutions.
By implementing these advanced instruments, industries not only enhance compliance with strict regulatory standards but also improve operational efficiency and product quality.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Electromagnetic Flow Meter
When selecting an electromagnetic flow meter, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance for your specific application. Firstly, the process conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the fluid are paramount. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, over 40% of flow measurement inaccuracies stem from insufficient consideration of these operational parameters. For instance, fluids with high viscosity or those that are conductive can significantly influence flow meter readings, necessitating careful calibration and meter selection.
Additionally, the size of the process piping is crucial. The electromagnetic flow meter needs to be compatible with existing piping dimensions to maintain accuracy and prevent issues like turbulence that could skew readings. Research from the European Flow Measurement Association indicates that a mismatch of flow meter size can lead to discrepancies of up to 20% in flow measurement results. Furthermore, understanding the installation environment, including factors such as accessibility for maintenance and the potential for interference from electromagnetic fields, is essential. A well-suited flow meter not only enhances accuracy but also contributes to lower operational costs over time by reducing maintenance needs and improving efficiency.
Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Electromagnetic Flow Meter
This bar chart illustrates the importance rating of various factors to consider when selecting an electromagnetic flow meter, ranging from accuracy to calibration, on a scale of 1 to 10.
Comparing Types of Electromagnetic Flow Meters Available in the Market
When selecting the right electromagnetic flow meter, understanding the various types available in the market is crucial. Electromagnetic flow meters can be broadly categorized into two types: contact-type and non-contact type. Contact-type meters, which utilize electrodes to measure fluid conductivity, are commonly found in industrial applications due to their accuracy and reliability. A report from the International Society of Automation suggests that contact-type electromagnetic flow meters account for approximately 85% of the market share, primarily attributed to their ability to handle a wide range of conductive fluids, including slurries and sewage.
On the other hand, non-contact electromagnetic flow meters, which use advanced technologies such as Doppler principles, are gaining traction, especially in applications involving non-conductive fluids. These devices can be advantageous where maintaining the integrity of the fluid is paramount, as they minimize potential contamination. Emerging data from the Global Market Insights reports that the demand for non-contact flow meters is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6% from 2023 to 2030, indicating a shift towards more innovative and adaptable solutions in flow measurement technologies. Understanding these distinctions will help users align their selection with specific application requirements.
Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Electromagnetic Flow Meter for Your Needs
| Type of Flow Meter | Suitable Applications | Operating Temperature Range | Accuracy | Typical Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inline Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Water and wastewater management | -20°C to 80°C | ±0.2% of reading | $1,000 - $5,000 |
| Compact Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Chemical processing | -10°C to 90°C | ±0.5% of reading | $2,000 - $7,000 |
| Insertion Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Large diameter pipelines | 0°C to 50°C | ±1.0% of reading | $500 - $3,000 |
| High-Temperature Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Steam and high-temperature liquids | -20°C to 180°C | ±0.3% of reading | $3,500 - $10,000 |
| Battery-Powered Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Remote monitoring | -30°C to 60°C | ±1.0% of reading | $1,500 - $6,000 |
| PTFE-Lined Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Corrosive liquids | -10°C to 80°C | ±0.5% of reading | $2,500 - $8,000 |
| Submersible Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Water level monitoring | 0°C to 50°C | ±1.0% of reading | $800 - $4,000 |
| Multivariable Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Complex process measurements | -20°C to 120°C | ±0.2% of reading | $4,000 - $12,000 |
| Portable Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Field testing and validation | -10°C to 50°C | ±1.5% of reading | $1,200 - $3,500 |
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Electromagnetic Flow Meters
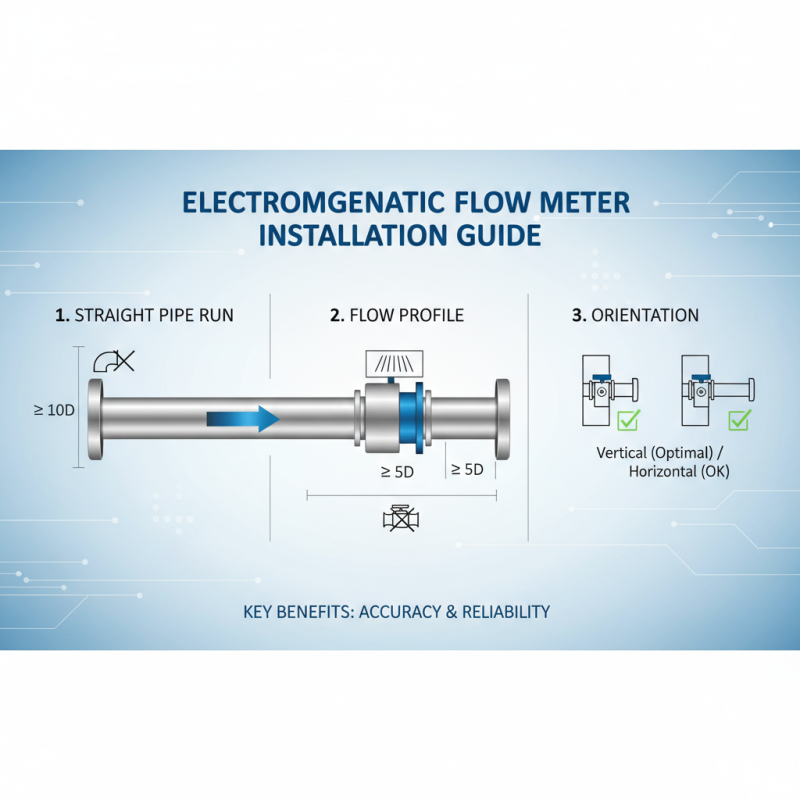
When it comes to installing electromagnetic flow meters, proper selection of the installation site is crucial for optimal performance. These devices are designed to work best in straight sections of pipe, free from bends, valves, or obstructions. It's essential to ensure that the meter is installed at a point where the flow profile is fully developed, usually a minimum distance of ten pipe diameters upstream and five downstream from any disturbances. Additionally, the orientation of the meter should be considered; most electromagnetic flow meters perform optimally when installed vertically, although they can also work well horizontally under the right conditions.
Maintenance of electromagnetic flow meters is relatively straightforward, but it is vital to follow prescribed maintenance schedules to ensure long-term reliability. Regular inspections should focus on verifying the calibration and ensuring that the electrodes are free of build-up, which can impede accuracy. Cleaning the meter might involve flushing the pipeline to remove any debris, especially in applications with potential sediment or impurities in the fluid. Monitoring the electronics and connections is also crucial, as loose wiring or corrosion can lead to erratic readings. By adhering to these installation and maintenance tips, users can maximize the performance and lifespan of their electromagnetic flow measurement systems.
Related Posts
-

The Future of Flow Meters Technology Trends and Their Impact on Industrial Efficiency
-

Top 10 Flow Rate Meters for Accurate Measurement and Performance Evaluation
-

5 Reasons Why the 2 Inch Flow Meter is a Game Changer for Your Industry
-

How to Choose the Right Mag Meter for Your Industrial Applications
-

10 Best Electromagnetic Flow Meters for Accurate Fluid Measurement
-

How to Choose the Right Electromagnetic Flow Meter for Your Application
