How to Choose the Right Flow Rate Meter for Your Application
In today's industrial landscape, the accurate measurement of fluid flow is critical for optimizing processes, ensuring quality control, and maintaining efficiency. A key component in achieving this precision is the selection of an appropriate Flow Rate Meter. According to recent industry reports, the global flow meter market is projected to reach USD 8.6 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2021. This growth emphasizes the increasing reliance on flow measurement technologies across various sectors, including oil and gas, water and wastewater, and food and beverage industries.
Selecting the right Flow Rate Meter requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific application needs. Factors such as the type of fluid being measured, flow rate range, installation environment, and required accuracy must be considered. Recent findings indicate that improper selection not only hampers operational efficiency but can also lead to significant financial losses. Consequently, industries are increasingly investing in advanced flow measurement techniques, underlining the necessity for professionals to stay informed about the latest developments and technologies in flow measurement.
As businesses strive to enhance their operational efficacy, the ability to choose the most suitable Flow Rate Meter becomes paramount. In this guide, we will explore the essential criteria and considerations that can aid in making an informed decision, ensuring that your flow measurement needs are met with the utmost precision and accuracy.

Understanding Different Flow Rate Meter Types and Their Applications
When selecting a flow rate meter for your application, it's essential to understand the various types available and their specific functionalities. Common types include positive displacement meters, which are ideal for measuring viscous fluids, and turbine meters, which are suited for low-viscosity liquids in cleaner industrial environments. Electromagnetic flow meters, on the other hand, can handle conductive liquids and are widely used in water treatment processes. Each type of meter has distinct advantages that cater to different scenarios, such as accuracy, flow range, and installation requirements.
**Tips:** When deciding on a flow rate meter, consider the fluid characteristics like temperature, viscosity, and conductivity. This insight helps ensure the meter you choose will provide reliable and accurate readings for your specific conditions. Additionally, look into the installation requirements and maintenance needs of each meter type, as these factors can affect long-term efficiency and operation costs.
Another consideration is the flow measurement range. Some meters perform better with specific flow rates, so it’s crucial to assess both the lower and upper limits of your application. Make sure the meter can handle any fluctuations in flow to avoid measurement inaccuracies. Lastly, think about the environment in which the meter will be used; factors like pressure and potential exposure to harsh conditions may dictate your choice and the type of materials best suited for your application.
Key Parameters for Selecting a Flow Rate Meter: Accuracy and Range
When selecting a flow rate meter for a specific application, two of the most critical parameters to consider are accuracy and range. Accuracy refers to the degree of closeness of the measured flow rate to the actual value, and it is vital in applications where precision is essential, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing or food processing. According to recent industry data, flow meters with an accuracy range of ±0.5% of the reading are increasingly favored in high-stakes environments, ensuring that the measured flow aligns closely with the desired specifications.
Range, on the other hand, is defined as the span of flow rates that the meter can accurately measure. A broader range allows for flexibility in various applications, enabling a single meter to cover different flow conditions. Industry reports indicate that flow meters with a rangeability ratio of at least 10:1 are highly desirable, as they can accommodate fluctuating flow rates without compromising measurement accuracy. For instance, in wastewater treatment facilities, where flow rates can vary significantly, meters with a wide operational range can effectively adapt to changes while providing reliable data.
Ultimately, when choosing a flow rate meter, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your application, focusing on how accuracy and range align with operational needs. Evaluating these key parameters can lead to more efficient processes and improved overall performance in your industry.
Flow Rate Meter Accuracy and Range Comparison
Evaluating Fluid Characteristics: Viscosity, Density, and Temperature Impact
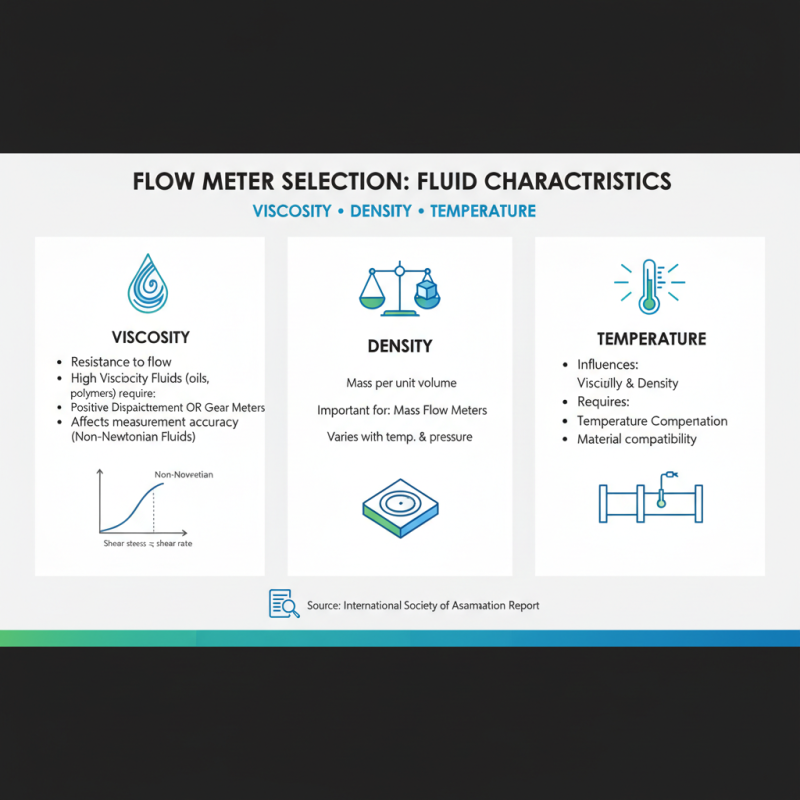
When selecting a flow rate meter for your application, understanding the fluid characteristics such as viscosity, density, and temperature is crucial. Viscosity, a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow, directly influences the choice of flow meter technology. For instance, fluids with high viscosity, such as oils or polymers, may require specialized flow meters like positive displacement or gear meters, which are designed to handle thicker liquids effectively. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, the viscosity of a fluid can significantly affect measurement accuracy, as conventional flow meters may struggle with non-Newtonian fluids that behave differently under varying shear rates.
Density, another key characteristic, impacts how flow meters respond to changes in pressure and temperature. Flow meters must be calibrated to account for differences in fluid density, which can vary due to temperature fluctuations. Data from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that a mere 1% change in temperature can lead to a density change of up to 0.5%, thus affecting flow measurements. Consequently, selecting a flow meter that can adapt to these variations is essential for maintaining precision in measurements and ensuring consistency in your process.
Temperature also plays a critical role in the performance of flow rate meters. Elevated temperatures can alter fluid characteristics and may lead to changes in viscosity and density. Reports from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers emphasize the importance of choosing meters that can withstand operational temperature ranges specific to your application. For instance, thermal mass flow meters are often selected for high-temperature applications due to their ability to maintain accuracy while operating under extreme conditions. Understanding these fluid characteristics will help ensure you choose the most appropriate flow rate meter for your needs, thereby enhancing the efficiency and reliability of your fluid measurement system.
Industry Standards and Specifications for Flow Rate Measurement
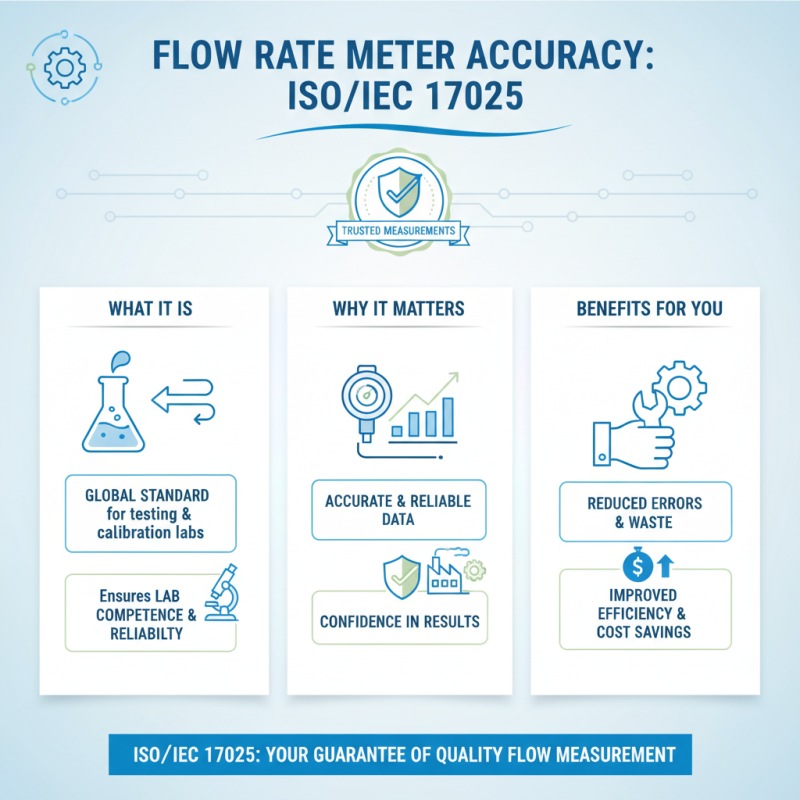
When selecting a flow rate meter for your application, it is essential to understand the relevant industry standards and specifications that ensure accurate and reliable measurements. One of the most recognized standards is the ISO/IEC 17025, which outlines the general requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. Adhering to this standard is crucial, as it guarantees that flow meters have been tested for accuracy and precision, providing users with confidence in the data collected.
Moreover, specific industries, such as oil and gas, often adhere to the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards, which detail the methods and equipment required for accurate flow measurement in hydrocarbon applications. According to API’s guidelines, utilizing flow meters that meet these standards can improve operational efficiency and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Additionally, organizations like the International Trade Association (ITA) highlight that approximately 25% of measuring inaccuracies in flow meters can significantly impact overall production costs—emphasizing the necessity of standards in selecting appropriate instruments.
Ultimately, understanding the applicable standards, such as the European Organization for Standardization (EN) specifications, can also play a critical role in flow measurement accuracy. These specifications provide guidelines on temperature and pressure conditions, ensuring that selected flow rate meters will perform reliably across varying operational environments. By aligning your choice of flow meter with these established standards, you can enhance measurement reliability and optimize your processes accordingly.
Comparative Analysis: Cost versus Performance of Flow Rate Meters
When selecting a flow rate meter, weighing the cost against performance is crucial for ensuring efficient operations in various applications. While cheaper meters can save initial investment costs, their long-term performance and reliability may lead to hidden expenses. Consideration of factors such as calibration accuracy, maintenance needs, and the environmental conditions in which the meter operates will ultimately influence overall costs. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including repairs and operations, can provide a clearer picture of the investment's real value.
Tips for choosing the right flow rate meter include assessing your specific application requirements, such as the type of fluid being measured and the temperature and pressure conditions. It’s also beneficial to conduct a cost-benefit analysis that includes not just the purchase price, but also the expected lifespan and operation costs of the meter. Often, slightly more expensive meters with high accuracy and low maintenance can lead to greater savings over time, particularly in industries where process efficiency is critical.
Additionally, before making a decision, it’s advisable to consult with industry experts or utilize case studies of comparable applications. This will provide insights into how different flow meters perform under similar conditions and help you make an informed choice that balances both cost and performance effectively.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Flow Rate Meters for Accurate Measurement and Performance Evaluation
-

2025 Top 10 In Line Flow Meters: Enhance Accuracy and Efficiency
-

Innovative Alternatives to Inline Flow Meter Solutions for Enhanced Measurement Accuracy
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Flow Meters and Their Impact on Industrial Efficiency
-

5 Reasons Why the 2 Inch Flow Meter is a Game Changer for Your Industry
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Clamp On Water Flow Meter for Your Needs
