What is a 2 Inch Flow Meter? Essential Guide for Selection and Usage
In the realm of fluid management, understanding the various instrumentation available is crucial for ensuring efficiency and accuracy. One key component that often stands at the forefront of discussions is the 2 Inch Flow Meter. This essential device is designed to measure the flow rate of liquids and gases in a range of industrial applications, providing vital information for monitoring and controlling fluid processes. Its 2-inch diameter makes it suitable for moderate flow conditions, delivering precise measurements that are essential for optimizing performance and minimizing waste.
Choosing the right flow meter can be a daunting task, given the numerous options available on the market. However, the 2 Inch Flow Meter stands out due to its versatility and reliability, making it a popular choice among engineers and facility managers. Whether used in water treatment plants, chemical processing, or food and beverage production, this flow meter ensures consistent performance and allows for easy integration into existing systems. In this essential guide, we will delve into the key features, selection criteria, and best practices for using a 2 Inch Flow Meter, ultimately helping users make informed decisions and maximize the effectiveness of their fluid management systems.

Understanding the Basics of a 2 Inch Flow Meter
A 2 inch flow meter is an essential instrument used to measure the flow rate of liquids and gases in various applications. Understanding its basics is crucial for anyone involved in engineering, manufacturing, or environmental monitoring. Flow meters come in different types, including mechanical, electromagnetic, and ultrasonic, each suited for specific purposes. The size of a flow meter, such as 2 inches, often refers to the diameter of the pipe connection, which directly impacts its accuracy and capacity.
When selecting a 2 inch flow meter, consider factors such as the type of fluid being measured, the required accuracy, and the environmental conditions. For example, if you are measuring corrosive substances, a meter with appropriate materials is essential. Additionally, understanding the flow profile and whether the installation location may affect measurement is vital.
**Tips:** Always ensure the flow meter is installed correctly for accurate readings; improper installation can lead to errors in measurements. Regular maintenance and calibration can help maintain the device's performance over time, ensuring reliable operation. Lastly, familiarize yourself with the manufacturer's specifications to choose the right model that meets your operational needs.
What is a 2 Inch Flow Meter? Essential Guide for Selection and Usage
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Size | 2 Inches |
| Flow Range | 10 - 200 GPM |
| Accuracy | ± 1% of Full Scale |
| Connection Type | Flanged or Threaded |
| Application | Water, Oil, Chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 80°C |
| Materials | Stainless Steel, PVC |
| Power Supply | Battery or AC Power |
Key Features and Specifications of 2 Inch Flow Meters
A 2-inch flow meter is a crucial instrument designed for measuring the flow rate of liquids and gases in various industrial applications. When selecting a flow meter, several key features and specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First, the type of flow meter—whether it be electromagnetic, ultrasonic, or mechanical—will determine its appropriateness for specific fluids and conditions. For instance, electromagnetic flow meters are ideal for conductive liquids, while ultrasonic meters can effectively measure non-conductive fluids.
Another important specification is the meter's accuracy and calibration. Most 2-inch flow meters offer accuracies ranging from ±0.5% to ±2% of the reading, which is essential for precise measurement and monitoring. Additionally, the flow range, pressure rating, and temperature tolerance should align with the fluid characteristics and the system's operational needs. Users should also consider the ease of installation and maintenance, as well as any digital features that enhance data logging and remote monitoring capabilities. These factors collectively play a vital role in selecting the right flow meter to ensure efficiency and sustained performance in fluid management systems.
2 Inch Flow Meter Data Comparison
This chart compares the flow rates of different types of 2 inch flow meters under varying conditions. The data represents the flow rate (in gallons per minute) for each meter type.
Types of 2 Inch Flow Meters: Choosing the Right Type
When selecting a 2-inch flow meter, understanding the various types available is crucial to making an informed decision. The most common types include electromagnetic flow meters, turbine flow meters, and positive displacement flow meters, each with distinct advantages and applications. Electromagnetic flow meters utilize Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction, making them ideal for measuring conductive liquids in large volumes with high accuracy. They require minimal maintenance and provide a reliable measurement in harsh conditions.
On the other hand, turbine flow meters are suitable for clean, low-viscosity fluids, as they operate by measuring the rotational speed of a turbine placed in the flow stream. Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for many industrial applications. Lastly, positive displacement flow meters are known for their accuracy and ability to handle viscous fluids. They work by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and then counting how many times that volume passes through the meter. This type of flow meter is particularly effective for applications where precise measurement is critical. Each type has unique features that cater to specific needs, making it essential to evaluate your requirements before choosing the right 2-inch flow meter.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a 2 Inch Flow Meter
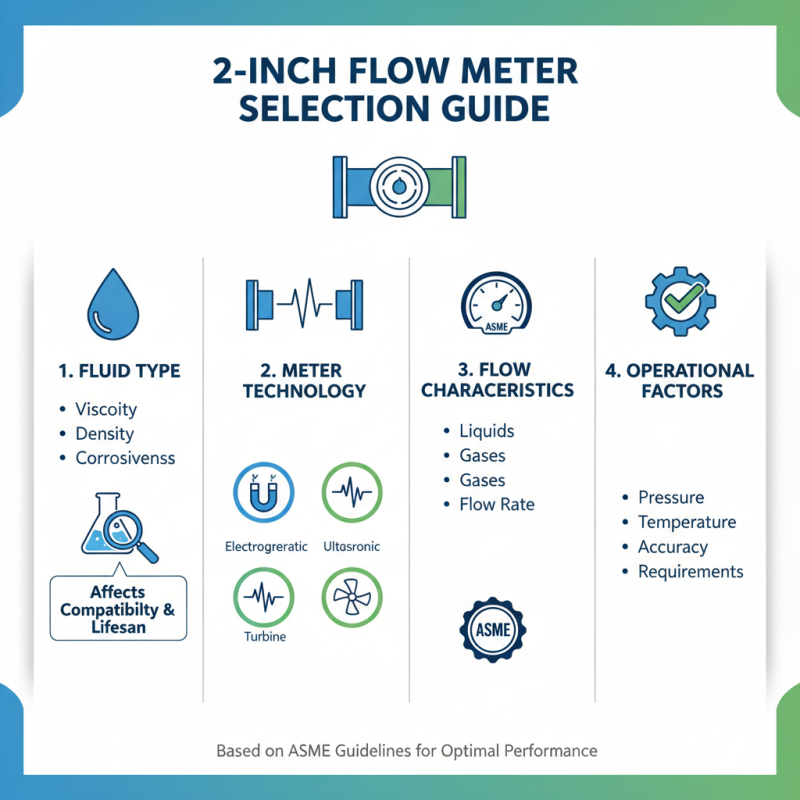
When selecting a 2-inch flow meter, several critical factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. The first consideration is the type of fluid being measured. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), the flow characteristics of different liquids (and gases) affect the choice of meter type—whether it be electromagnetic, ultrasonic, or turbine flow meters. The viscosity, density, and corrosiveness of the fluid can all influence the meter's compatibility and lifespan.
Another vital aspect is the flow rate range. The flow meter should be capable of handling both minimum and maximum flow rates efficiently, which can significantly impact measurement accuracy. According to a report by the Flow Measurement Institute, flow meters that are improperly sized can result in deviations of up to 20% in readings. It's also essential to assess installation considerations such as space constraints and whether a straight run of piping is available, which can impact the installation effectiveness and the overall accuracy of the flow measurements. Ensuring that your selection process encompasses these factors will lead to a more reliable and accurate flow measurement system.
Best Practices for Installing and Maintaining 2 Inch Flow Meters
When it comes to installing and maintaining a 2 inch flow meter, adherence to best practices is crucial for ensuring accuracy and longevity. First, proper installation begins with selecting an appropriate location that minimizes turbulence and obstructions in the flow. The meter should be placed straight away from bends, valves, and other disturbances in the piping system. Ensuring the meter is level and securely mounted will also contribute to more reliable readings.
Regular maintenance is key to sustaining the performance of a 2 inch flow meter. Periodic inspection for leaks and wear is essential, as even minor issues can lead to significant inaccuracies. It is advisable to clean the meter regularly, especially if it is measuring fluids prone to sediment or buildup. Additionally, calibrating the flow meter at regular intervals ensures that it operates within its specified accuracy range, helping to prevent costly errors in measurement.
Following these best practices will enhance the flow meter's reliability and efficiency in various applications.
Related Posts
-

In Depth Comparison of 2 Inch Flow Meters for Diverse Industrial Applications
-

5 Reasons Why the 2 Inch Flow Meter is a Game Changer for Your Industry
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right 2 Inch Flow Meter in Your Industry
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Clamp On Water Flow Meter for Your Needs
-

Top 10 Flow Meters: Industry Trends & Efficiency Data You Need to Know
-

Understanding Flow Transmitters: The Key to Accurate Fluid Measurement in Industrial Applications
